Params¶
Params enable you to provide runtime configuration to tasks. You can configure default Params in your DAG code and supply additional Params, or overwrite Param values, at runtime when you trigger a DAG. Param values are validated with JSON Schema. For scheduled DAG runs, default Param values are used.
Also defined Params are used to render a nice UI when triggering manually. When you trigger a DAG manually, you can modify its Params before the dagrun starts. If the user-supplied values don’t pass validation, Airflow shows a warning instead of creating the dagrun.
DAG-level Params¶
To add Params to a DAG, initialize it with the params kwarg.
Use a dictionary that maps Param names to either a Param or an object indicating the parameter’s default value.
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.models.param import Param
with DAG(
"the_dag",
params={
"x": Param(5, type="integer", minimum=3),
"my_int_param": 6
},
):
Task-level Params¶
You can also add Params to individual tasks.
def print_my_int_param(params):
print(params.my_int_param)
PythonOperator(
task_id="print_my_int_param",
params={"my_int_param": 10},
python_callable=print_my_int_param,
)
Task-level params take precedence over DAG-level params, and user-supplied params (when triggering the DAG) take precedence over task-level params.
Referencing Params in a Task¶
Params can be referenced in templated strings under params. For example:
PythonOperator(
task_id="from_template",
op_args=[
"{{ params.my_int_param + 10 }}",
],
python_callable=(
lambda my_int_param: print(my_int_param)
),
)
Even though Params can use a variety of types, the default behavior of templates is to provide your task with a string.
You can change this by setting render_template_as_native_obj=True while initializing the DAG.
with DAG(
"the_dag",
params={"my_int_param": Param(5, type="integer", minimum=3)},
render_template_as_native_obj=True
):
This way, the Param’s type is respected when it’s provided to your task:
# prints <class 'str'> by default
# prints <class 'int'> if render_template_as_native_obj=True
PythonOperator(
task_id="template_type",
op_args=[
"{{ params.my_int_param }}",
],
python_callable=(
lambda my_int_param: print(type(my_int_param))
),
)
Another way to access your param is via a task’s context kwarg.
def print_x(**context):
print(context["params"]["my_int_param"])
PythonOperator(
task_id="print_my_int_param",
python_callable=print_my_int_param,
)
JSON Schema Validation¶
Param makes use of JSON Schema, so you can use the full JSON Schema specifications mentioned at https://json-schema.org/draft/2020-12/json-schema-validation.html to define Param objects.
with DAG(
"my_dag",
params={
# an int with a default value
"my_int_param": Param(10, type="integer", minimum=0, maximum=20),
# a required param which can be of multiple types
# a param must have a default value
"multi_type_param": Param(5, type=["null", "number", "string"]),
# an enum param, must be one of three values
"enum_param": Param("foo", enum=["foo", "bar", 42]),
# a param which uses json-schema formatting
"email": Param(
default="example@example.com",
type="string",
format="idn-email",
minLength=5,
maxLength=255,
),
},
):
Note
As of now, for security reasons, one can not use Param objects derived out of custom classes. We are planning to have a registration system for custom Param classes, just like we’ve for Operator ExtraLinks.
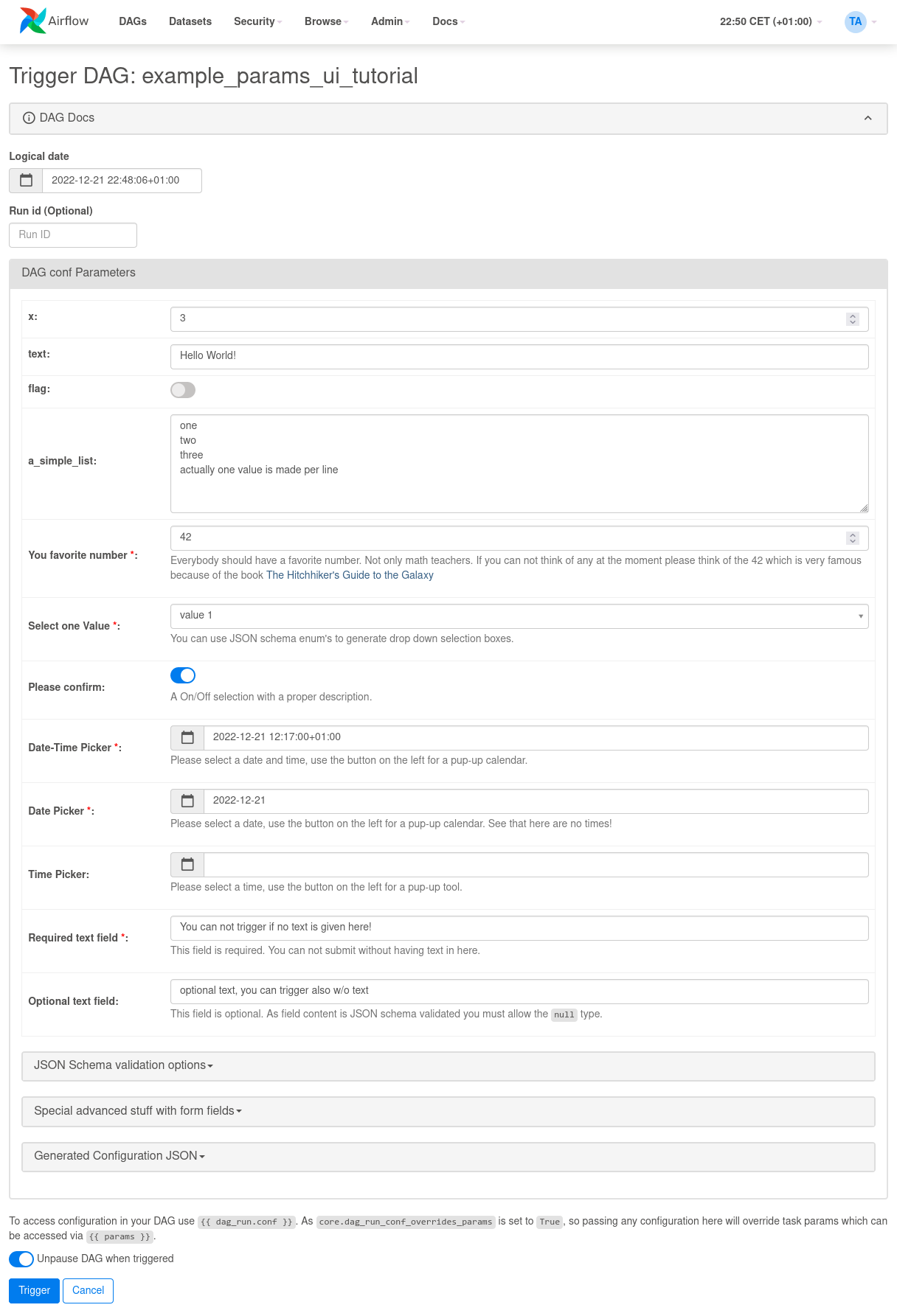
Use Params to Provide a Trigger UI Form¶
DAG level params are used to render a user friendly trigger form.
This form is provided when a user clicks on the “Trigger DAG w/ config” button.
The Trigger UI Form is rendered based on the pre-defined DAG Prams. If the DAG has no params defined, a JSON entry mask is shown.
The form elements can be defined with the Param class and attributes define how a form field is displayed.
The following features are supported in the Trigger UI Form:
Direct scalar values (boolean, int, string, lists, dicts) from top-level DAG params are interpreted and render a corresponding field type. The name of the param is used as label and no further validation is made, all values are treated as optional.
If you use the
Paramclass as definition of the param value, the following parameters can be added:The Param attribute
titleis used to render the form field label of the entry boxThe Param attribute
descriptionis rendered below an entry field as help text in gray color. Note that if you want to provide HTML tags for special formatting or links you need to use the Param attributedescription_html, see tutorial DAGexample_params_ui_tutorialfor an example.The Param attribute
typeinfluences how a field is rendered. The following types are supported:string: Generates a text box to edit text. You can add the parametersminLengthandmaxLengthto restrict the text length.numberorinteger: Generates a field which restricts adding numeric values only. You can add the parametersminimumandmaximumto restrict number range accepted.boolean: Generates a toggle button to be used asTrueorFalse.date,datetimeandtime: Generate date and/or time pickerarray: Generates a HTML multi line text field, every line edited will be made into a string array as valueobject: Generates a JSON entry fieldNote: Per default if you specify a type, a field will be made required with input - because of JSON validation. If you want to have a field value being added optional only, you must allow JSON schema validation allowing null values via:
type=["null", "string"]
The Param attribute
enumgenerates a drop-down select list. As of JSON validation, a value must be selected.If a form field is left empty, it is passed as
Nonevalue to the params dict.Form fields are rendered in the order of definition.
If you want to add sections to the Form, add the parameter
sectionto each field. The text will be used as section label. Fields w/osectionwill be rendered in the default area. Additional sections will be collapsed per default.If you want to have params not being displayed, use the
constattribute. These Params will be submitted but hidden in the Form.On the bottom of the form the generated JSON configuration can be expanded. If you want to change values manually, the JSON configuration can be adjusted. Changes are overridden when form fields change.
If you want to render custom HTML as form on top of the provided features, you can use the
custom_html_formattribute.
For examples also please take a look to two example DAGs provided: example_params_trigger_ui and example_params_ui_tutorial.
Disabling Runtime Param Modification¶
The ability to update params while triggering a DAG depends on the flag core.dag_run_conf_overrides_params.
Setting this config to False will effectively turn your default params into constants.
