AWS Secrets Manager Backend¶
To enable Secrets Manager, specify SecretsManagerBackend
as the backend in [secrets] section of airflow.cfg. These backend_kwargs are parsed as JSON, hence Python
values like the bool False or None will be ignored, taking for those kwargs the default values of the secrets backend.
Here is a sample configuration:
[secrets]
backend = airflow.providers.amazon.aws.secrets.secrets_manager.SecretsManagerBackend
backend_kwargs = {
"connections_prefix": "airflow/connections",
"connections_lookup_pattern": null,
"variables_prefix": "airflow/variables",
"variables_lookup_pattern": null,
"config_prefix": "airflow/config",
"config_lookup_pattern": null,
"profile_name": "default"
}
To authenticate you can either supply arguments listed in Amazon Webservices Connection Extra config or set environment variables.
[secrets]
backend = airflow.providers.amazon.aws.secrets.secrets_manager.SecretsManagerBackend
backend_kwargs = {
"connections_prefix": "airflow/connections",
"variables_prefix": "airflow/variables",
"config_prefix": "airflow/config",
"role_arn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789098:role/role-name"
}
Storing and Retrieving Connections¶
There are two ways to store Airflow connections in AWS Secrets Manager.
Storing a Connection as a URI¶
You can store the connection as an Airflow connection URI:
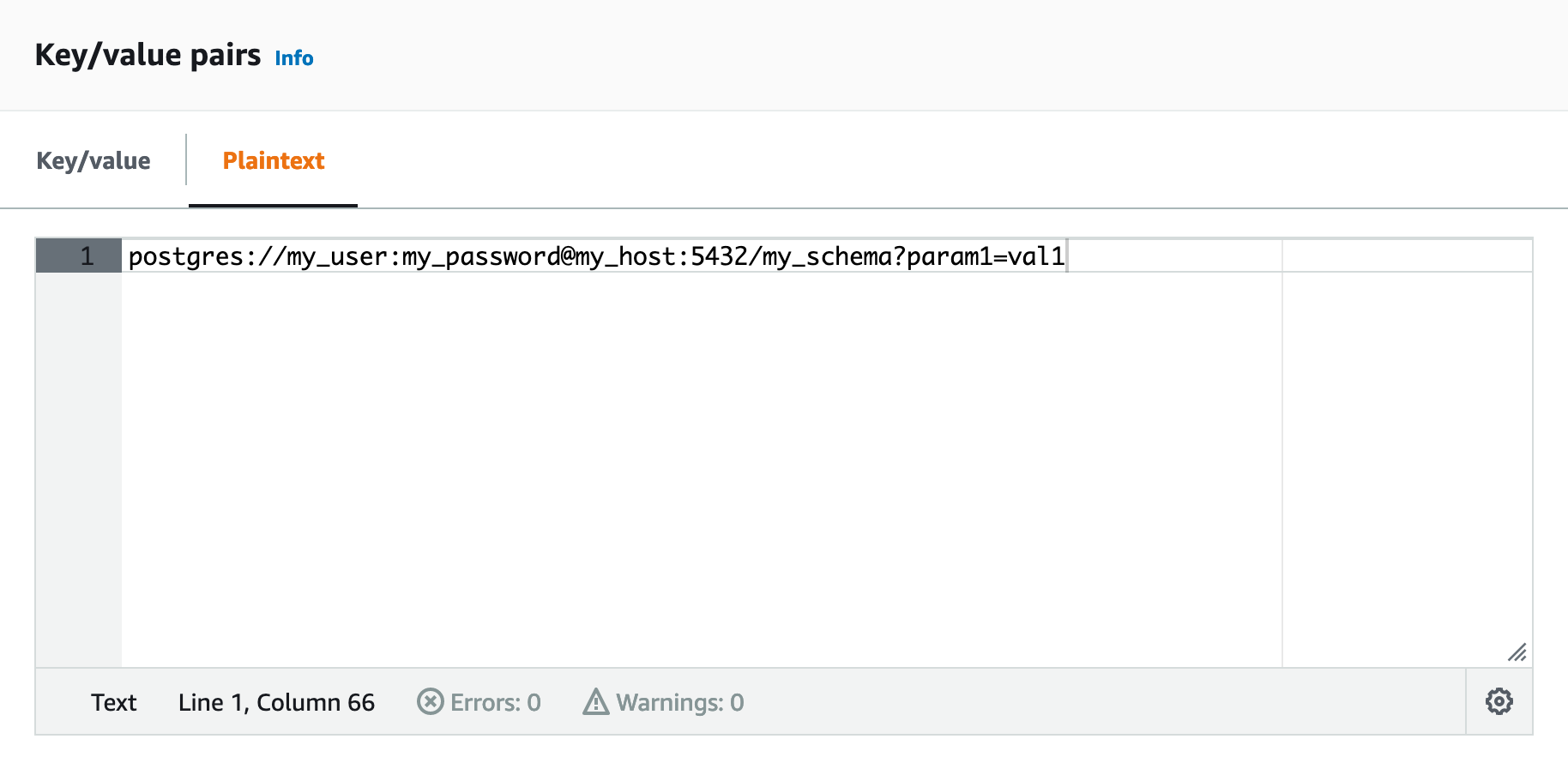
Note that every field is assumed to be URL-encoded if you store the connection as a URI.
For example, if you want to use the value my password, in the URI, it should be represented as my%20password.
Storing a Connection as a JSON¶
You can also store the connection as a JSON with the appropriate key-value pairs:
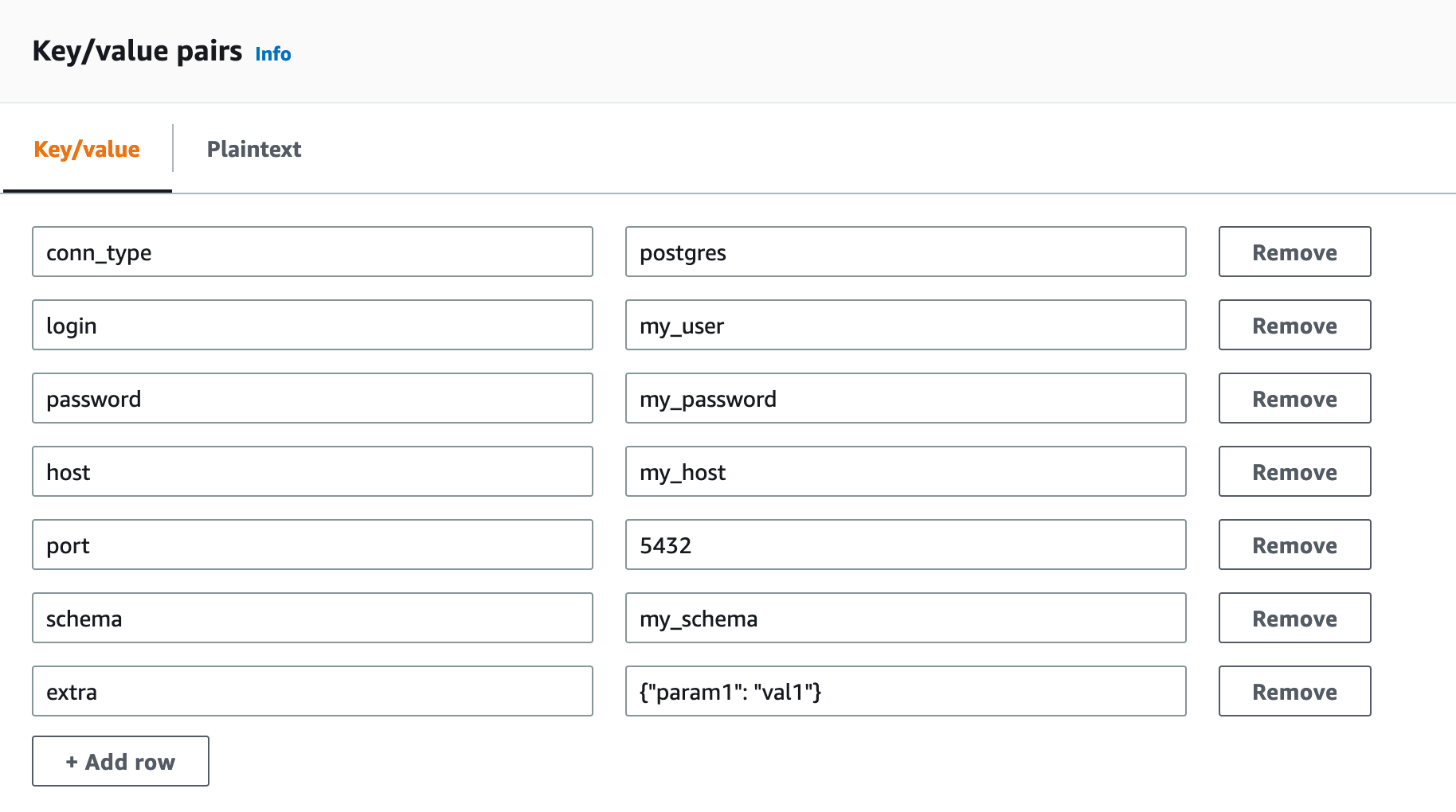
Using Airflow default names for connection fields is encouraged, but different aliases are allowed for each field:
Connection type:
conn_type,conn_id,connection_type,engineLogin:
login,user,username,user_namePassword:
password,pass,keyHost:
host,remote_host,serverPort:
portExtra:
extra. Note that this extra field should be a valid JSON.
More words can be added to the list using the parameter extra_conn_words in the configuration. This
parameter has to be a dict of lists with the following optional keys: user, password, host, schema, conn_type.
As an example, if you have set connections_prefix as airflow/connections, then for a connection id of smtp_default,
you would want to store your connection at airflow/connections/smtp_default. This can be done through the AWS web
console or through Amazon CLI as shown below:
aws secretsmanager put-secret-value \
--secret-id airflow/connections/smtp_default \
--secret-string '{"login": "nice_user", "password": "this_is_the_password", "host": "ec2.8399.com", "port": "999"}'
Verify that you can get the secret:
❯ aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id airflow/connections/smtp_default
{
"ARN": "arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-2:314524341751:secret:airflow/connections/smtp_default-7meuul",
"Name": "airflow/connections/smtp_default",
"VersionId": "34f90eff-ea21-455a-9c8f-5ee74b21be672",
"SecretString": "{\n \"login\":\"nice_user\",\n \"password\":\"this_is_the_password\"\n,
\n \"host\":\"ec2.8399.com\"\n,\n \"port\":\"999\"\n}\n",
"VersionStages": [
"AWSCURRENT"
],
"CreatedDate": "2020-04-08T02:10:35.132000+01:00"
}
If you don’t want to use any connections_prefix for retrieving connections, set it as an empty string "" in the configuration.
Storing and Retrieving Variables¶
If you have set variables_prefix as airflow/variables, then for a Variable key of hello,
you would want to store your Variable at airflow/variables/hello.
Optional lookup¶
Optionally connections, variables, or config may be looked up exclusive of each other or in any combination. This will prevent requests being sent to AWS Secrets Manager for the excluded type.
If you want to look up some and not others in AWS Secrets Manager you may do so by setting the relevant *_prefix parameter of the ones to be excluded as null.
For example, if you want to set parameter connections_prefix to "airflow/connections" and not look up variables and config, your configuration file should look like this:
[secrets]
backend = airflow.providers.amazon.aws.secrets.secrets_manager.SecretsManagerBackend
backend_kwargs = {
"connections_prefix": "airflow/connections",
"variables_prefix": null,
"config_prefix": null,
"profile_name": "default"
}
If you want to only lookup a specific subset of connections, variables or config in AWS Secrets Manager, you may do so by setting the relevant *_lookup_pattern parameter.
This parameter takes a Regex as a string as value.
For example, if you want to only lookup connections starting by “m” in AWS Secrets Manager, your configuration file should look like this:
[secrets]
backend = airflow.providers.amazon.aws.secrets.secrets_manager.SecretsManagerBackend
backend_kwargs = {
"connections_prefix": "airflow/connections",
"connections_lookup_pattern": "^m",
"profile_name": "default"
}
Example of storing Google Secrets in AWS Secrets Manager¶
For connecting to a google cloud connection, all the fields must be in the extra field. For example:
If you are using the key file:
{"extra": {"key_path": "/opt/airflow/service_account.json",
"scope": "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_only"}}
If you are using the key dictionary.
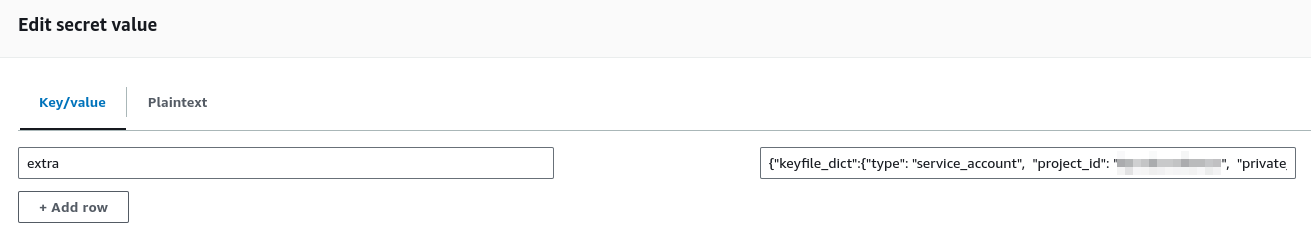
{"extra": {"keyfile_dict": "<copy & paste the service account json here>",
"scope": "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_only"}}
Either way you can edit the Key/value pairs directly on the UI