Logging and Monitoring architecture¶
Airflow supports a variety of logging and monitoring mechanisms as shown below.
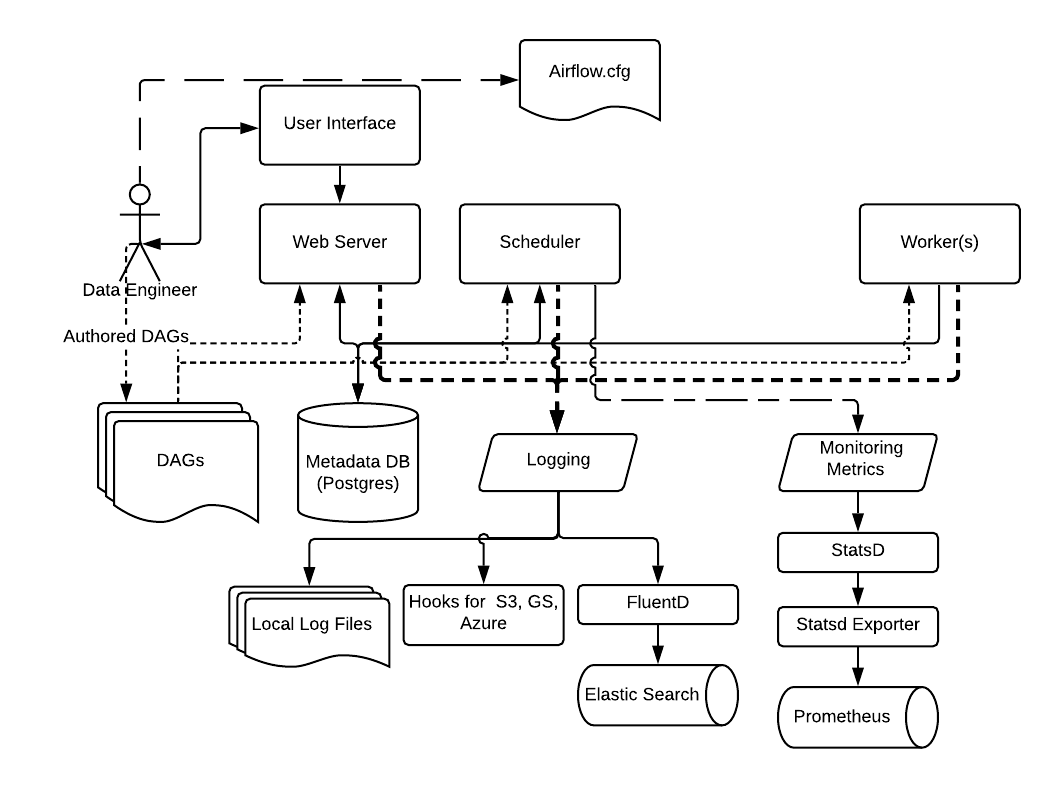
By default, Airflow supports logging into the local file system. These include logs from the Web server, the Scheduler, and the Workers running tasks. This is suitable for development environments and for quick debugging.
For cloud deployments, Airflow also has task handlers contributed by the Community for logging to cloud storage such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
The logging settings and options can be specified in the Airflow Configuration file, which as usual needs to be available to all the Airflow process: Web server, Scheduler, and Workers.
You can customize the logging settings for each of the Airflow components by specifying the logging settings in the Airflow Configuration file, or for advanced configuration by using advanced features.
For production deployments, we recommend using FluentD to capture logs and send it to destinations such as ElasticSearch or Splunk.
Note
For more information on configuring logging, see Logging for Tasks
Similarly, we recommend using StatsD for gathering metrics from Airflow and send them to destinations such as Prometheus.
Note
For more information on configuring metrics, see Metrics
