DAG Serialization¶
In order to make Airflow Webserver stateless (almost!), Airflow >=1.10.7 supports DAG Serialization and DB Persistence.
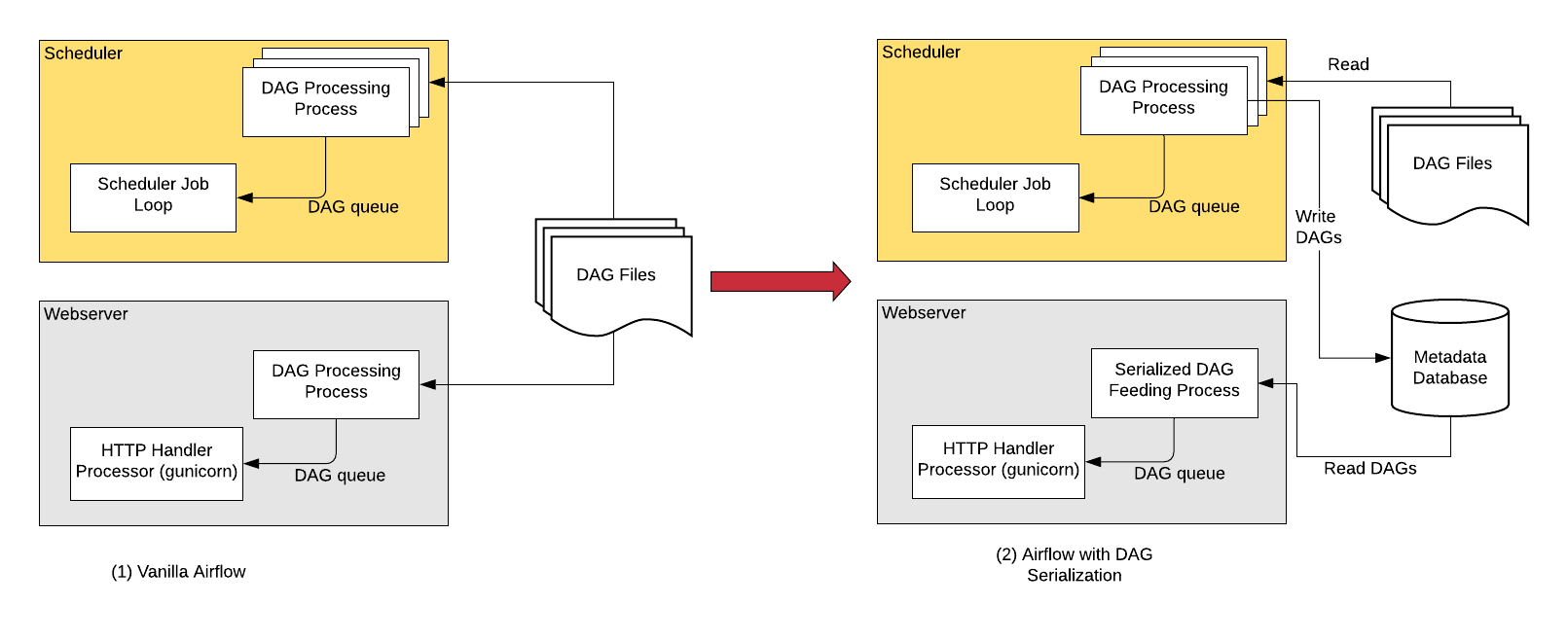
Without DAG Serialization & persistence in DB, the Webserver and the Scheduler both needs access to the DAG files. Both the scheduler and webserver parses the DAG files.
With DAG Serialization we aim to decouple the webserver from DAG parsing which would make the Webserver very light-weight.
As shown in the image above, when using the this feature, the Scheduler parses the DAG files, serializes them in JSON format and saves them in the Metadata DB.
The Webserver now instead of having to parse the DAG file again, reads the serialized DAGs in JSON, de-serializes them and create the DagBag and uses it to show in the UI.
One of the key features that is implemented as the part of DAG Serialization is that instead of loading an entire DagBag when the WebServer starts we only load each DAG on demand from the Serialized Dag table. This helps reduce Webserver startup time and memory. The reduction is notable when you have large number of DAGs.
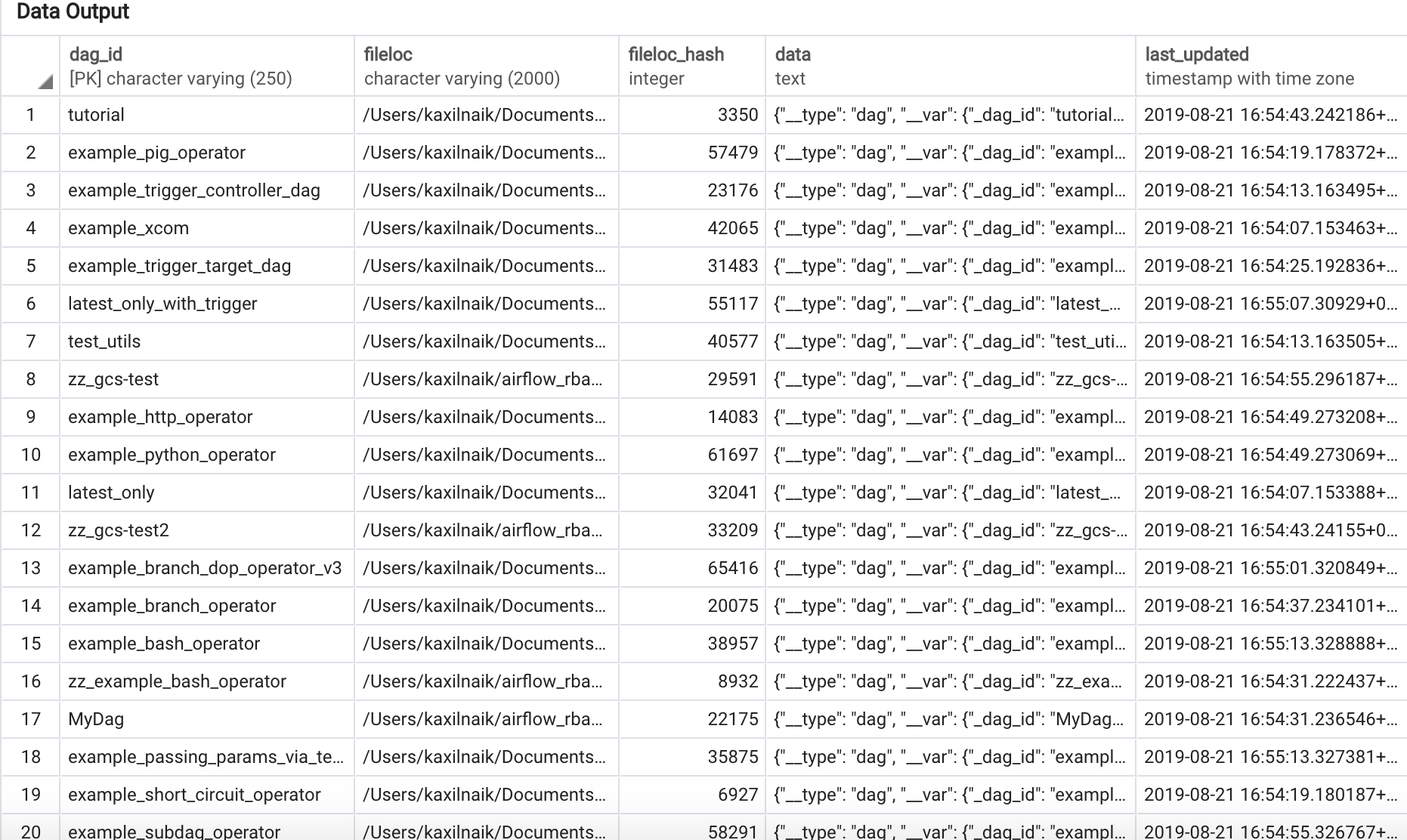
Below is the screenshot of the serialized_dag table in Metadata DB:
Enable Dag Serialization¶
Add the following settings in airflow.cfg:
[core]
store_serialized_dags = True
min_serialized_dag_update_interval = 30
store_serialized_dags: This flag decides whether to serialises DAGs and persist them in DB. If set to True, Webserver reads from DB instead of parsing DAG filesmin_serialized_dag_update_interval: This flag sets the minimum interval (in seconds) after which the serialized DAG in DB should be updated. This helps in reducing database write rate.
If you are updating Airflow from <1.10.7, please do not forget to run airflow db upgrade.
Limitations¶
The Webserver will still need access to DAG files in the following cases, which is why we said “almost” stateless.
Rendered Template tab will still have to parse Python file as it needs all the details like the execution date and even the data passed by the upstream task using Xcom.
Code View will read the DAG File & show it using Pygments. However, it does not need to Parse the Python file so it is still a small operation.
Using a different JSON Library¶
To use a different JSON library instead of the standard json library like ujson, you need to
define a json variable in local Airflow settings (airflow_local_settings.py) file as follows:
import ujson
json = ujson