Managing Connections¶
Airflow needs to know how to connect to your environment. Information
such as hostname, port, login and passwords to other systems and services is
handled in the Admin->Connections section of the UI. The pipeline code you
will author will reference the ‘conn_id’ of the Connection objects.
Connections can be created and managed using either the UI or environment variables.
See the Connections Concepts documentation for more information.
Creating a Connection with the UI¶
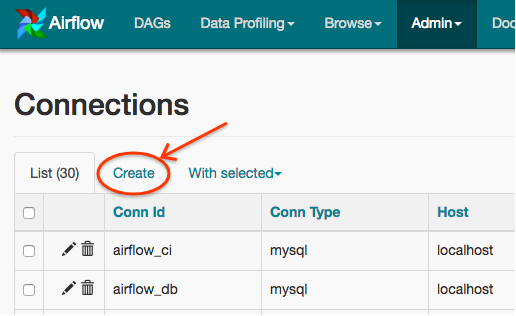
Open the Admin->Connections section of the UI. Click the Create link
to create a new connection.
Fill in the
Conn Idfield with the desired connection ID. It is recommended that you use lower-case characters and separate words with underscores.Choose the connection type with the
Conn Typefield.Fill in the remaining fields. See Connection Types for a description of the fields belonging to the different connection types.
Click the
Savebutton to create the connection.
Editing a Connection with the UI¶
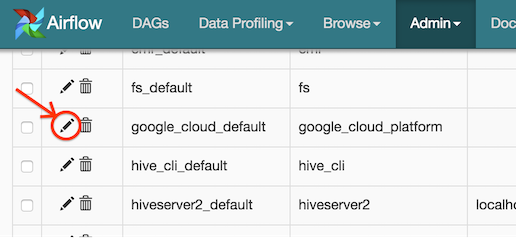
Open the Admin->Connections section of the UI. Click the pencil icon next
to the connection you wish to edit in the connection list.
Modify the connection properties and click the Save button to save your
changes.
Creating a Connection from the CLI¶
You may add a connection to the database from the CLI.
Obtain the URI for your connection (see Generating a Connection URI).
Then add connection like so:
airflow connections --add --conn_id 'my_prod_db' --conn_uri 'my-conn-type://login:password@host:port/schema?param1=val1¶m2=val2'
Alternatively you may specify each parameter individually:
airflow connections --add \
--conn_id 'my_prod_db' \
--conn_login 'login' \
--conn_password 'password' \
...
Storing a Connection in Environment Variables¶
The environment variable naming convention is AIRFLOW_CONN_<conn_id>, all uppercase.
So if your connection id is my_prod_db then the variable name should be AIRFLOW_CONN_MY_PROD_DB.
Note
Single underscores surround CONN. This is in contrast with the way airflow.cfg
parameters are stored, where double underscores surround the config section name.
The value of this environment variable must use airflow’s URI format for connections. See the section Generating a Connection URI for more details.
Using .bashrc (or similar)¶
If storing the environment variable in something like ~/.bashrc, add as follows:
export AIRFLOW_CONN_MY_PROD_DATABASE='my-conn-type://login:password@host:port/schema?param1=val1¶m2=val2'
Using docker .env¶
If using with a docker .env file, you may need to remove the single quotes.
AIRFLOW_CONN_MY_PROD_DATABASE=my-conn-type://login:password@host:port/schema?param1=val1¶m2=val2
Alternative secrets backend¶
In addition to retrieving connections from environment variables or the metastore database, you can enable an alternative secrets backend to retrieve connections. For more details see Alternative secrets backend
Connection URI format¶
In general, Airflow’s URI format is like so:
my-conn-type://my-login:my-password@my-host:5432/my-schema?param1=val1¶m2=val2
The above URI would produce a Connection object equivalent to the following:
Connection(
conn_id='',
conn_type='my_conn_type',
login='my-login',
password='my-password',
host='my-host',
port=5432,
schema='my-schema',
extra=json.dumps(dict(param1='val1', param2='val2'))
)
You can verify a URI is parsed correctly like so:
>>> from airflow.models.connection import Connection
>>> c = Connection(uri='my-conn-type://my-login:my-password@my-host:5432/my-schema?param1=val1¶m2=val2')
>>> print(c.login)
my-login
>>> print(c.password)
my-password
Generating a connection URI¶
To make connection URI generation easier, the Connection class has a
convenience method get_uri(). It can be used like so:
>>> import json
>>> from airflow.models.connection import Connection
>>> c = Connection(
>>> conn_id='some_conn',
>>> conn_type='mysql',
>>> host='myhost.com',
>>> login='myname',
>>> password='mypassword',
>>> extra=json.dumps(dict(this_param='some val', that_param='other val*')),
>>> )
>>> print(f"AIRFLOW_CONN_{c.conn_id.upper()}='{c.get_uri()}'")
AIRFLOW_CONN_SOME_CONN='mysql://myname:mypassword@myhost.com?this_param=some+val&that_param=other+val%2A'
Additionally, if you have created a connection via the UI, and you need to switch to an environment variable, you can get the URI like so:
from airflow.hooks.base_hook import BaseHook
conn = BaseHook.get_connection('postgres_default')
print(f"AIRFLOW_CONN_{conn.conn_id.upper()}='{conn.get_uri()}'")